Advanced Techniques to Prevent Infection
Advanced Wound Care MethodsWound care has greatly evolved, shifting from traditional methods to advanced techniques. These techniques enhance healing, reduce complications, and improve patient experiences. Our understanding of wound biology and healing processes has deepened, allowing us to implement effective recovery strategies. This post explores advanced wound care methods, their benefits, and management tips for better outcomes.
Understanding Advanced Wound Care
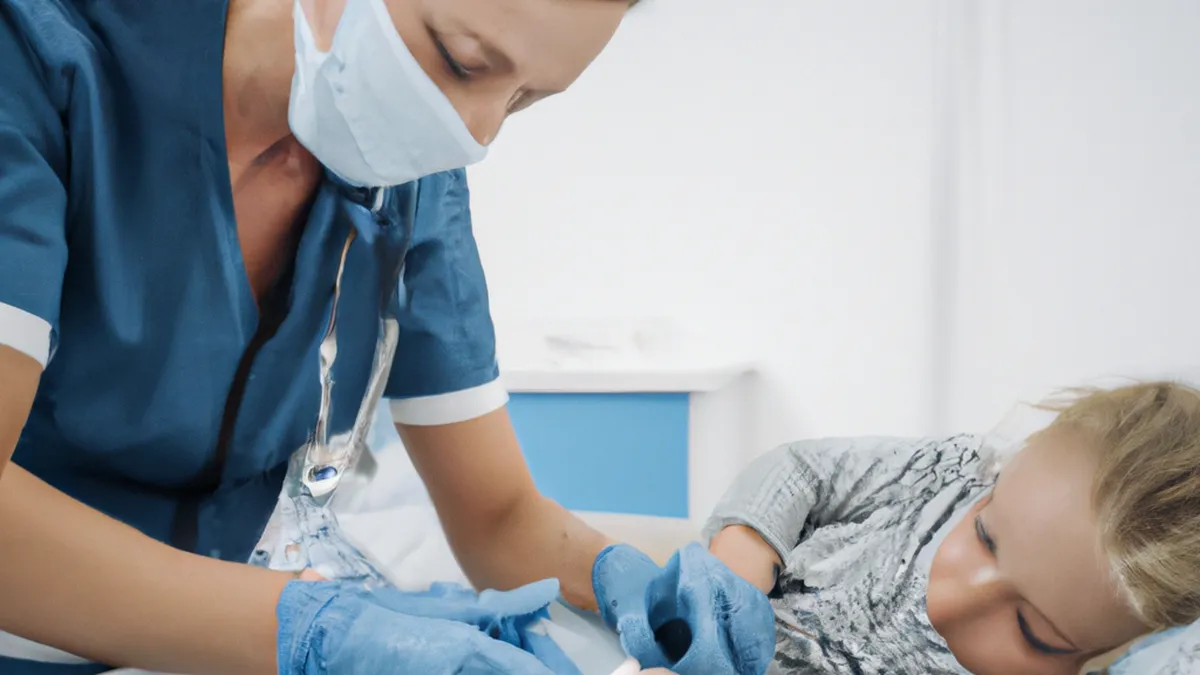
Advanced wound care includes specialized treatments that surpass standard care protocols. These methods effectively address chronic wounds, diabetic ulcers, surgical incisions, and complex injuries. Techniques like Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT), bioengineered skin substitutes, advanced dressings, and cellular therapies play critical roles in modern wound management.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT)
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) stands out as one of the most effective advanced wound care methods. This technique uses a vacuum dressing to create a controlled negative pressure environment around the wound. NPWT removes excess fluid, reduces edema, increases blood flow, and stimulates granulation tissue formation. Research shows NPWT can accelerate healing by up to 50%, especially for complex or chronic wounds.To apply NPWT, practitioners place a specialized foam or gauze dressing over the wound and attach a vacuum pump. The pump continuously draws out fluid, lowering infection risk and promoting a moist healing environment. Patients usually find this method comfortable, alleviating pressure and pain.
Bioengineered Skin Substitutes
Bioengineered skin substitutes represent another innovative advancement in wound care. These products mimic the structure and function of natural skin, providing scaffolding for tissue regeneration. They often include living cells, growth factors, and extracellular matrix components that aid healing in chronic wounds like diabetic foot ulcers or severe burns.For example, dermal matrices frequently assist when traditional treatments fail. These substitutes promote faster healing, reduce infection risk, and minimize scarring. By creating a suitable environment for skin cells to grow and migrate, bioengineered skin substitutes significantly enhance wound healing.
Advanced Dressings
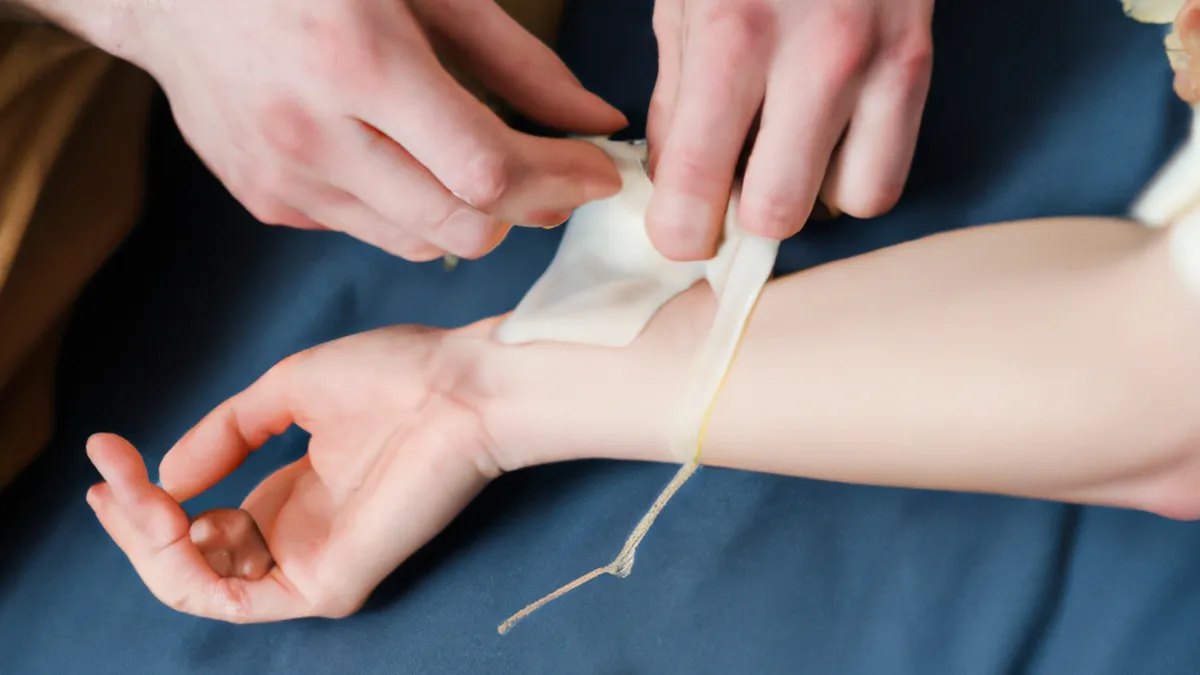
Advanced dressings play a vital role in modern wound management. Unlike traditional gauze, these dressings maintain optimal moisture levels, provide thermal insulation, and protect wounds from contaminants. Options include hydrocolloid, alginate, and foam dressings, tailored for various wound types.- **Hydrocolloid Dressings**: Ideal for low to moderately exuding wounds, they create a moist environment and offer a protective barrier against bacteria.- **Alginate Dressings**: Derived from seaweed, alginate dressings absorb heavily and suit wounds with significant exudate. They control moisture levels and encourage healing.
Conclusion
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Gear tip: consider sports first aid kit, kt tape, and blister pads to support this topic.
In summary, advanced wound care methods significantly improve healing and patient outcomes. Implementing these techniques can enhance recovery for various wound types.
Below are related products based on this post:
FAQ
What are advanced wound care methods?
Advanced wound care methods include specialized treatments that go beyond standard care protocols. These techniques effectively address chronic wounds, diabetic ulcers, surgical incisions, and complex injuries, leading to improved healing and patient outcomes.
How does Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) work?
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) uses a vacuum dressing to create a controlled negative pressure environment around the wound. This method removes excess fluid, reduces edema, increases blood flow, and stimulates granulation tissue formation, accelerating healing by up to 50% for complex wounds.
What are bioengineered skin substitutes?
Bioengineered skin substitutes mimic the structure and function of natural skin, providing scaffolding for tissue regeneration. They often contain living cells and growth factors that help heal chronic wounds, promoting faster recovery and reducing infection risk.













Post Comment