Maximizing Recovery: The Role of Sleep in Optimizing Athletic Performance

# Maximizing Recovery: The Role of Sleep in Optimizing Athletic Performance
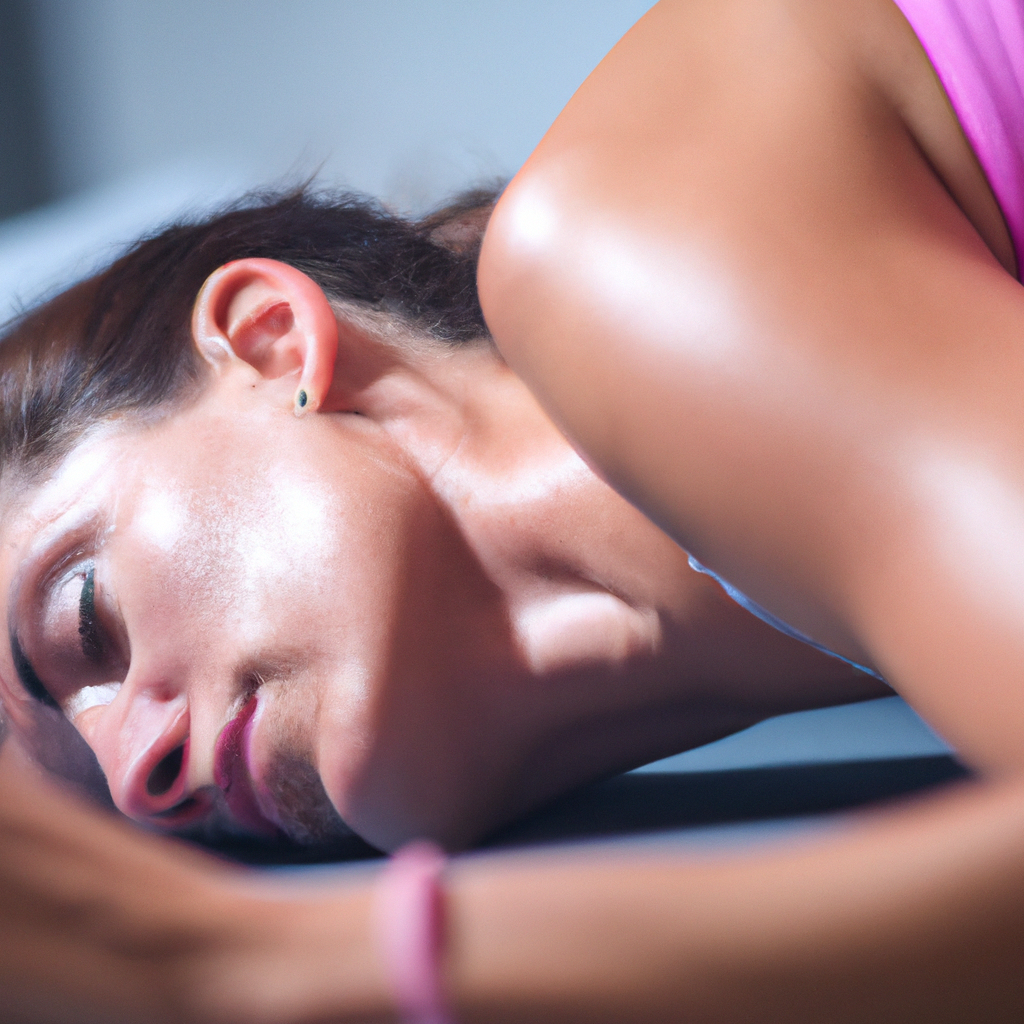
In the world of athletics, the pursuit of peak performance is a relentless endeavor. Athletes train rigorously, pushing their physical and mental boundaries to achieve their goals. However, amidst the sweat, discipline, and perseverance, one crucial aspect is often overlooked: sleep. Sleep is not merely a passive state of rest; it is an active period of recovery, repair, and rejuvenation. In this blog post, we will explore the vital role sleep plays in optimizing athletic performance, provide nutrition and exercise advice for enhancing sleep quality, and highlight the numerous health benefits associated with adequate rest.
## The Importance of Sleep for Athletes
Sleep is essential for every individual, but for athletes, it is a game-changer. A study published in the *Journal of Sports Sciences* found that sleep deprivation can lead to decreased performance, impaired cognitive function, and increased risk of injury. During deep sleep, the body undergoes critical processes that aid in muscle recovery, hormone regulation, and overall health maintenance.
One of the primary benefits of sleep is the release of growth hormone, which is vital for muscle repair and growth. When athletes sleep, their bodies work to rebuild tissues damaged during intense training, making sleep a cornerstone of recovery. Furthermore, sleep plays a significant role in energy metabolism, helping athletes maintain optimal performance levels during training and competition.
## Nutrition Tips for Better Sleep
1. **Prioritize Whole Foods**: A diet rich in whole foods can positively influence sleep quality. Foods high in magnesium, such as leafy greens, nuts, and seeds, help with muscle relaxation and promote sleep.
2. **Limit Caffeine and Sugar**: Consuming caffeine or sugary snacks close to bedtime can disrupt sleep patterns. Aim to limit caffeine intake in the afternoon and avoid high-sugar foods or drinks in the evening.
3. **Hydration Matters**: Staying hydrated throughout the day is important, but try to limit fluid intake close to bedtime to avoid waking up for bathroom visits. Dehydration can also lead to fatigue, making it harder to recover.
4. **Incorporate Sleep-Inducing Foods**: Foods rich in tryptophan, such as turkey, bananas, and oats, can help produce serotonin, a precursor to melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep. Including these foods in your evening meals can promote better sleep.
5. **Consider Timing**: Eating large meals right before bed can lead to discomfort and disrupt sleep. Aim to finish your last meal at least two to three hours before going to sleep.
## Exercise Advice for Enhancing Sleep Quality
1. **Incorporate Regular Physical Activity**: Regular exercise is known to improve sleep quality. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week. However, avoid vigorous workouts close to bedtime as they may energize you instead of promoting relaxation.
2. **Establish a Routine**: Consistency is key when it comes to sleep. Establishing a regular exercise routine can help regulate your body’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep at the same time each night.
3. **Mind-Body Practices**: Activities such as yoga and meditation can help reduce stress and promote relaxation, making it easier to wind down at the end of the day. Gentle stretching or breathing exercises before bed can also enhance sleep quality.
4. **Listen to Your Body**: While it’s essential to stay active, it’s equally important to recognize when your body needs a break. Overtraining can lead to fatigue and negatively impact sleep. Incorporate rest days and active recovery sessions into your training plan.
## Health Benefits of Adequate Sleep
The benefits of quality sleep extend beyond athletic performance. Here are some key health advantages:
1. **Enhanced Cognitive Function**: Adequate sleep improves concentration, decision-making, and reaction times—all crucial for athletes during competition.
2. **Mood Regulation**: Sleep plays a significant role in emotional regulation








Post Comment